The rise of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies slowly transforms the world of finance through the revolutionary presence of DeFi. AAVE is one of DeFi crypto projects that works as a decentralized lending system that allows users to lend, borrow and earn interest on crypto assets, without any necessary middlemen.
Aave was developed with the goal to address real world financial systems, especially access to banking services and lending facilities which comes with significant barriers, such as underserved regions, censorship resistance, heavy centralized authority, etc.
In this article we will explain what AAVE is. How does it work? And why it matters for decentralized finance systems.

Introduction
Back in 2017, before investors became aware of crypto DeFi projects existence, there was one DeFi project being developed, a project named ETHLend. ETHLend offers a fully decentralized peer to peer lending marketplace which uses the smart contract capability on the Ethereum blockchain while using digital tokens as collateral. Back in the day, crypto assets still lacked utility and adoptions.
The developers behind ETHLend were fascinated by the possibilities that smart contracts brought and are able to start various experiments for blockchain technology use cases. At first, ETHLend development was heavily focused on developing reliable smart contracts architecture and have strict values on the immutability of the code and decentralization.
Since its inception, ETHLend has grown to become a popular DeFi lending platform, and by 2018, ETHLend rebranded the project name as AAVE.
The rebranding then adopted a series of new features and ultimately changed the direction of DeFi projects’ development into become a more robust and user-friendly DeFi protocol.
How Does AAVE Work?
Traditionally, getting a loan required one to visit a bank or another financial institution. When applying for a loan, the bank will request a certain amount of collateral. In exchange for the loan. The borrower then pays back the loan to the bank gradually every month, plus interest.
AAVE on the other hand, runs on the Ethereum blockchain using Ethereum smart contracts functions that enables crypto assets to be managed by a distributed network of computers running the algorithm that AAVE developed. Similar to other DeFi projects, Aave users do not have to trust a particular entity to manage their funds. Users only need to trust the code will be executed properly.
Aave protocol enables the creation of lending pools that allow users to lend and/or borrow various cryptocurrency assets. Users may borrow cryptocurrencies up to a certain percentage of the collateral’s value they have deposited. This is known as the loan-to-value (LTV), and Aave limits the borrowed amount to 80% of the current value of the deposited collateral.
AAVE uses smart contracts to automate the borrowing process by determining the loan terms, collecting the deposited collateral, and distributing the cryptocurrency that is being borrowed. The smart contract code executed independently with its own code and rule without the intervention of intermediaries.
Borrowers then receive funds in the form of a special token known as an aToken, which its value is pegged to another asset. This token then encoded in order for the lenders to receive interest on their deposits.
As for the lenders, users can deposit crypto into the platform without taking a loan to earn interest from the borrowers of the deposited crypto.
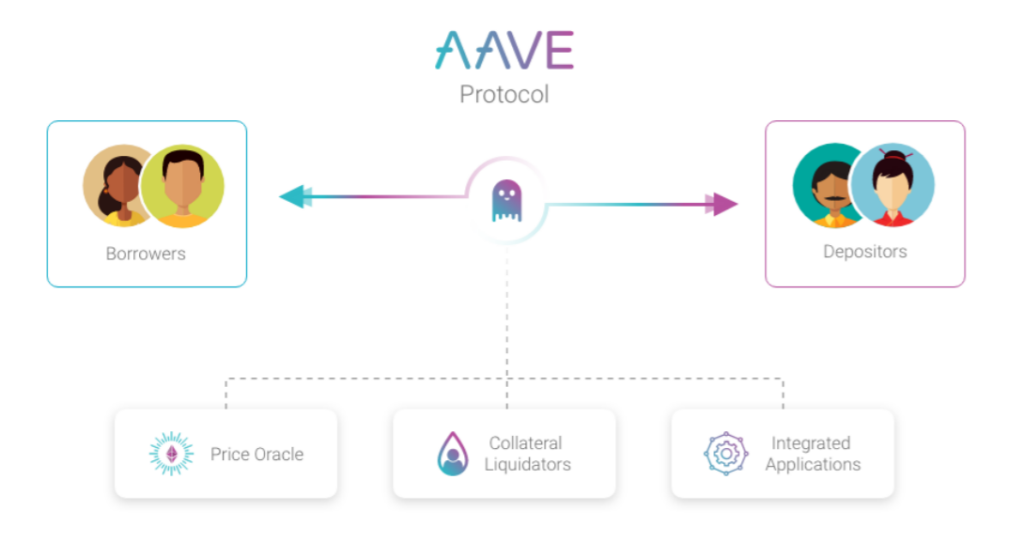
In simple words, here’s how AAVE lending market works
1. Depositors (Lenders) deposit AAVE supported crypto assets into the AAVE protocols
2. Lenders then earn aTokens as a proof that they have deposited funds inside AAVE protocols. This aTokens is interest bearing token which generating interest return to lenders
3. Lenders may let AAVE protocol works continuously to generate interest, or lenders can borrow funds from AAVE to their needs
4. When lenders want to borrow funds, they are able to borrow up to 80% of their deposited funds from before. For example when they lend 100 USDC to AAVE, they will earn 100 aUSDC in return, and able to borrow up to 80 USDC using aUSDC as collateral
5. Borrowers can pay back their borrowed funds + interest back to AAVE or use the funds on other protocols
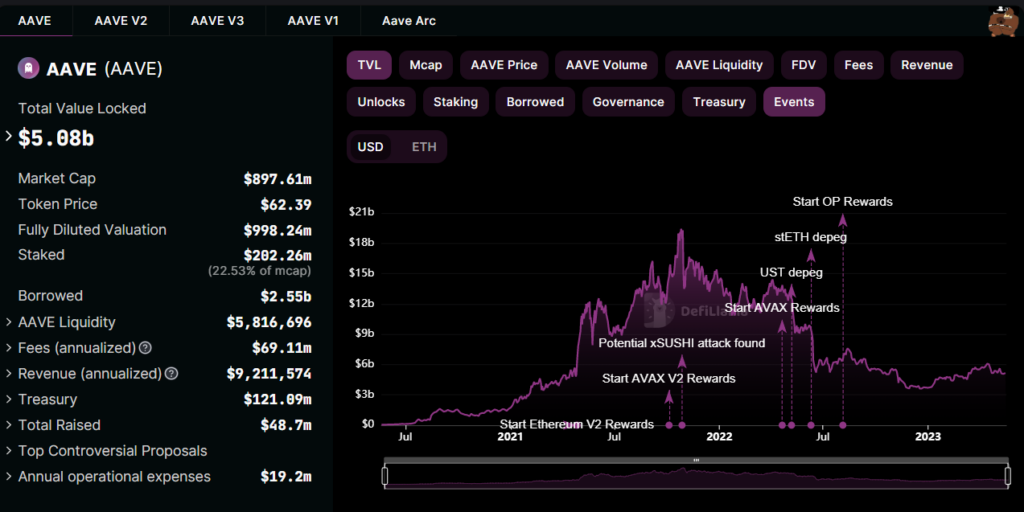
As of now, there are a total of $5,1 billion total value locked (TVL) on AAVE protocol across 7 different chains.
Flash Loans
AAVE has a unique feature known as Flash Loan that distinguished AAVE as a leading technical innovator in DeFi space.
A flash loan is an instant loan with one condition, it must be repaid within the same Ethereum transaction block. Aave Flash Loan procedure occurs within a single Ethereum transaction and depends on the ability of Ethereum transactions to revert, rendering all commands invalid and void if the borrowed capital is not repaid.
For example, If $1 million worth of tokens are borrowed and the conditions of the loan are not met, the technical architecture of the Ethereum network will void the transaction. Flash Loans are intended for programmers to create smart contracts that enable flash loans, make an exchange, and repay the loans all in the same Ethereum transaction block.
Aave Flash Loans is an experimental finance tool that is not used on any other blockchain platform besides Ethereum. Most notable use case of flash loans is to avoid the risk of being liquidated while exchanging volatile crypto assets. For example, If users borrow USDC while using ETH as collateral and the price of ETH was crashing, the borrower would be in danger of loan liquidation. In this situation, the borrower can use a Flash Loan to swap their volatile ETH asset for a stablecoin. The collateral value would now be stable, and borrowers would avoid all risks of being liquidated.
Who Created AAVE?
Stani Kulechov is the lead developer and CEO of AAVE. Kulechov earned a master degree in law from the University of Helsinki in 2018, and was a member of the Legal Aid Committee while at the University of Helsinki. He then worked in the legal profession until late 2017.
Ethereum and the concept of smart contracts encouraged him to establish a decentralized financial ecosystem and improve the efficiency of financial products. Later, Kulechov founded ETHLend in 2017, until it was rebranded to AAVE in 2018. In January 2020, the Aave protocol was officially released on the Ethereum mainnet.
AAVE Major Upgrades
● AAVE v1
The first AAVE lending market protocols on the Ethereum network.
● AAVE v2
Aave v2 improves many aspects over v1, opening a variety of new design spaces for developers to build products and services. In Aave v2, all positions are tokenized, wide adoption of WETH tokens instead of ETH, flash loans within the protocol.
● AAVE v3
In this upgrade, AAVE introduced Portal, which allows crypto assets to seamlessly flow between AAVE v3 markets over different networks, various risk management improvements, and specific to Layer 2 networks user experience and reliability improvements.
The AAVE Token
AAVE protocol has its own native token called AAVE (previously LEND). AAVE token serves several functions within the AAVE ecosystem, such as grant the communities governance rights of AAVE protocol, paying protocol’s transaction fees, and earn staking rewards if users stake AAVE token into the protocol.
AAVE has an initial supply of 13 million tokens which are redeemable by LEND holders with a ratio of 100 LEND per 1 AAVE back in 2018. Now there are 14,4 million circulating AAVE tokens with a maximum supply of 16 million tokens. The remaining 3 million tokens will be allocated to the AAVE Reserve and controlled by the AAVE token holders, to incentivize the AAVE Ecosystem and development.
Currently, AAVE token is ranked on top 50 of cryptocurrency highest market cap with more than $900 million in valuation.
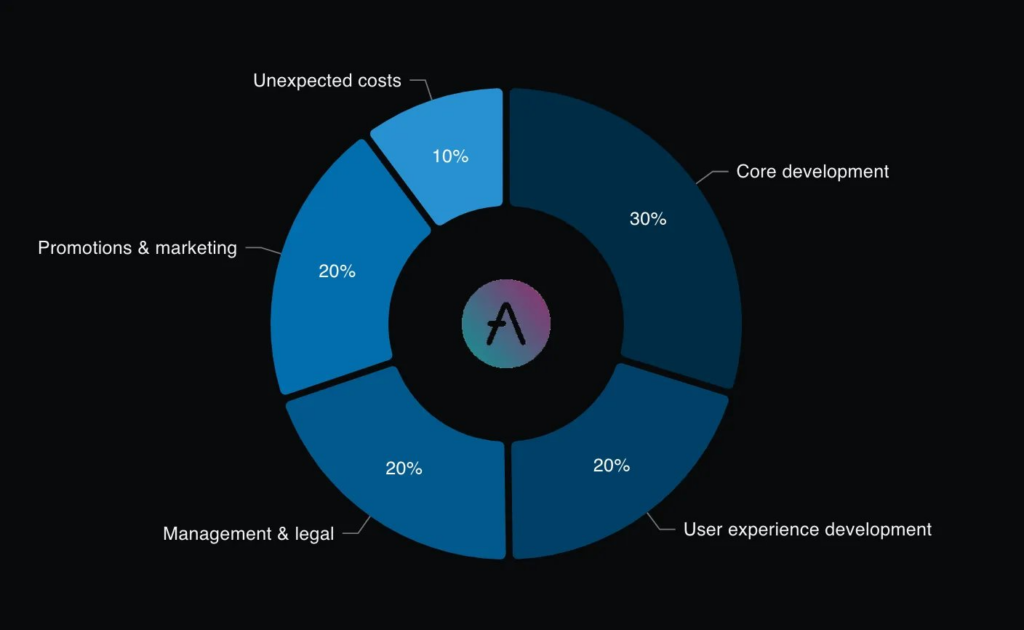
The initial token distribution of UNI token:
● 30% is allocated to Core Development
● 20% is allocated to User experience development
● 20% is allocated to Management and legal
● 20% is allocated to Promotions and marketing
● 10% is allocated to Unexpected and miscellaneous costs
Out of AAVE’s initial supply distribution, 23% went to the founders team and 77% to investors.
| Decentralized borrowing and lending platformAAVE provides a decentralized method for borrowing and lending activities. Operates using smart contracts on Ethereum blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and allows users to directly interact with the protocol |
| No KYC financing protocolAAVE empowers users by giving them control over their financial activities. Users can borrow assets without need to do KYC protocol, credit checks, or extensive documentation |
| Flexible borrowing optionsAAVE offers flexible borrowing options, such as variable interest rates that adjust based on supply and demand dynamics, and stable interest rates for more predictable borrowing costs |
| Multichain protocolAAVE operable on 7 different chains, such as Ethereum, Avalanche, Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, AAVE ARC, and Centrifuge RWA |
| Leading DeFi innovationAAVE developed the innovative flash loans, which enable users to borrow assets without collateral as long as the borrowed amount is returned within the same transaction. This opens up new possibilities for arbitrage, liquidity provision, and more. |
| GovernanceAs long as users have AAVE token, they can participate in governance and vote on upgrades, and new asset listings, displaying community-driven and decentralized governance model |
| Staking returnAAVE token holders can stake their tokens in the Aave Safety Module (ASM) to provide collateral for the protocol. In return, they earn staking rewards, denominated in AAVE tokens, incentivizing participation and contributing to the protocol’s security and stability |
| Risk of liquidationVolatile crypto assets as collateral may impose the risks of liquidation if the value falls. This means any collateral may be sold off when its value decreasing beyond certain amount |
| No insuranceAAVE does not offer insurance on its protocol, this means user funds are not protected. Lost funds or crypto sent to the wrong address will not be reimbursed |
| Smart contract bugsThere are risks of potential vulnerabilities or bugs in smart contract code. Smart contract bugs could lead to security breaches, hacking attempts, or loss of user funds |
| Regulatory pressureThe evolving regulatory landscape could result in changes or restrictions on every DeFi platforms, impacting the availability AAVE protocol in certain regions |
Closing
AAVE is a decentralized cryptocurrency lending platform where users can borrow and lend digital currencies that utilizes smart contracts functionality, which are automated agreements written on the blockchain. AAVE specializes in overcollateralized loans, meaning the amount of funds the users are able to borrow is less than the deposited digital assets. This ensures lenders are safe from potential losses caused by loan defaults and allows AAVE to sell the collateral if its value drops significantly.
However, it’s important to be aware of certain risks associated with the protocol. The smart contracts powering AAVE could potentially be compromised, proper security measures are essential to mitigate this risk and ensure the safety of funds.









