Many people are unaware of one blockchain limitation, which is sealed off from the outside world. This means the blockchain has no information about real world events outside its network (off-chain data). This limitation is known as the oracle problem. Any smart contract function written on the blockchain did not have access to real world information, such as the crypto price itself, stock price, etc.
So how does any Decentralized Exchange (DEX) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi) applications gain information regarding crypto price movements and events? This is achievable thanks to the Oracle. An oracle is a trusted source of external data that provides information to a smart contract. Oracle works similar to a bridge that connects the blockchain with real world information and events.
One of the popular Oracle service providers is Chainlink (LINK). Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides reliable and secure oracles into the blockchain or smart contract protocols. Chainlink aims to solve the problem of obtaining accurate and trustworthy external data for smart contracts.

How does Chainlink supply information into the blockchain? And how does it work in a decentralized approach? We will explain below.
Introduction
While billions of Dollars are spent and circling around the crypto space, there is one infrastructure that facilitates all the transactions, the Oracle. An oracle gathers data from external sources, such as websites or wikis, and securely provides it to the blockchain. It ensures that the information is accurate and can be trusted by the blockchain application. For example, a smart contract might need to know the certain crypto or stock prices, or sports scores to execute its tasks.
Oracles are responsible for fetching the necessary data and and and formatting that data so the blockchain can interpret the information.
This where Chainlink serves as an information-carrier oracle, it sends the information to the blockchain, where it may be accessed by smart contracts in order to make decisions or carry out specific actions based on the provided information.
The Chainlink network was launched in June 2017 by SmartContract.com company with the purpose as leading decentralized oracle network and allows developers to build Web3 applications with seamless access to real-world data and off-chain computation across all blockchain networks.
How Does Chainlink Work?
Chainlink was developed to enable highly secure and reliable automated data transfer between blockchains and external systems through smart contracts. Using a decentralized network of independent entities known as oracles that collectively retrieve data from multiple sources, aggregate it, and deliver a validated single data point to the smart contract in order to trigger its execution based on the provided data. Since Chainlink gathers data in a decentralized and collective manner by utilizing independent nodes, it ensures the accuracy of information compared to centralized single entity which may error to deliver the information.
For example, Chainlink provides the USD price of ETH crypto price to blockchains via the ETH/USD price feed oracles which uses numerous independent nodes and data sources to source and deliver the price data to the blockchain’s smart contract. This ETH/USD price oracle then can be used by smart contract programs to get the current price of ETH to be used as collateral to obtain a loan or to settle a prediction made about the future ETH price within specific DeFi apps.
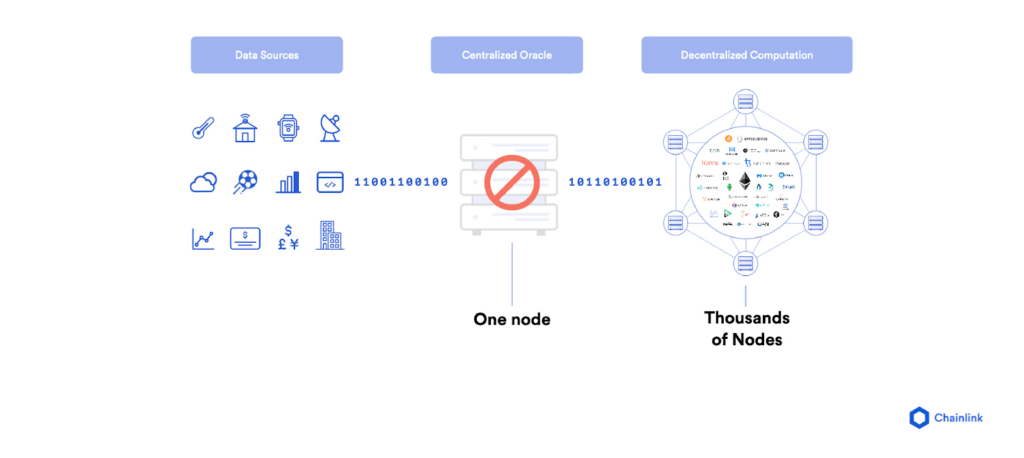
Chainlink divides its execution process into three steps to enable connectivity between its users and external data sources:
1. Oracle Selection
First, Chainlink oracles users start by making a request called a service-level agreement (SLA). This SLA includes details about the data they are required. Chainlink’s software uses this SLA information to find suitable oracles that can provide the requested data. Once the parameters are matched with the right oracles, the user submits the SLA and deposits their LINK cryptocurrency in an Order-Matching contract, which accepts bids from oracles.
2. Data Reporting
After that, the oracles connect with external sources and obtain the real world data requested in the SLA. The data is then processed by the oracles and sent back to contracts running on the Chainlink blockchain.
3. Aggregation
After the oracles collect the requested data, the next step is to combine the results altogether. The collected data is then sent to an Aggregation contract. This contract evaluates the validity of each data response and calculates a weighted score based on the combined data.
In order to provides multiple layers of security to ensure the users can trust the oracle network, Chainlink using three types of smart contracts:
1. Aggregating Contracts, which functions to collect data from oracles and match the most accurate results with the smart contract that required them.
2. Order-Matching Contract, which functions to match a smart contract’s service level agreement (SLA) with the best bidding oracles.
3. Reputation Contract, which verifies an oracle’s integrity by reviewing its track record, such as the total number of completed requests, average response time and amount of LINK cryptocurrency the oracle has staked.
Chainlink Use Cases
Since Chainlink oracle feeds are important and required element to smart contract, there are several use cases of Chainlink oracle to the entire cryptocurrency industry:
1. Highly required for Decentralized Exchanges operation
Chainlink oracles are commonly used in decentralized exchanges to provide real-time and accurate price feeds for various cryptocurrencies. These price feeds are crucial for determining exchange rates and executing trades on DEXs. Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network ensures the integrity and reliability of these price feeds.
2. DeFi platforms
DeFi protocols use Chainlink to price assets, access interest rates, verify collateralization, and many more, which enable these products to perform functions like issue a loan at balanced market value, automate the yield staking rewards, and contribute to settle many Decentralized Finance activities from its information.
3. Decentralized Insurance
Chainlink oracles has a use case in the crypto insurance industry. They enable insurers to obtain accurate and reliable data for risk assessment, claim validation, and policy payouts.
4. Tokenization and Asset Management
Chainlink oracles can be used to provide data on real-world assets that are tokenized on the blockchain. This data includes information about asset ownership, valuation, and market prices.
5. Gaming/NFT
Smart contract-based gaming applications on the blockchain which commonly use NFT as digital collectibles also required Chainlink. It serves as a source of randomness to generate random in-game scenarios or determine the lucky winner of prizes. Chainlink provides a randomness solution called VRF, which generates randomness and delivers it to the smart contract in a fair and unbiased manner.
Who Created Chainlink?
The Chainlink network was launched back in June 2017 by SmartContract.com company, founded by Steve Ellis and Sergey Nazarov. Steve Ellis, has experience in the finance and trading industry while Sergey Nazarov is a technology entrepreneur and has a background in building secure middleware systems.
Both co-funders then published Chainlink’s white paper in September 2017. While Chainlink are not the earliest oracle platform in the blockchain space, it has has gained significant popularity and widespread adoption due to its robust architecture, decentralized network, and focus on security and reliability.
The LINK Token
Chainlink oracle has its own native token called LINK. LINK token serves several functions within the Chainlink ecosystem, such as node incentives, means of payment for the oracle services, and grants the governance of the Chainlink network.
Currently, LINK is an inflationary asset since its supply keeps increasing to incentivize the node operators who provide information oracles. However, since LINK has a maximum supply of 1 billion tokens, LINK tokens will become deflationary assets.
LINK has Initial supply of 350 million of LINK tokens which was offered during the ICO phase back in 2017, and LINK has a maximum supply of 1 billion tokens. Currently, there are around 517 million circulating LINK tokens around the world.
As of now, LINK token is on the top 20 of the largest cryptocurrency based on its market cap which counts around $3,4 billion token valuation.
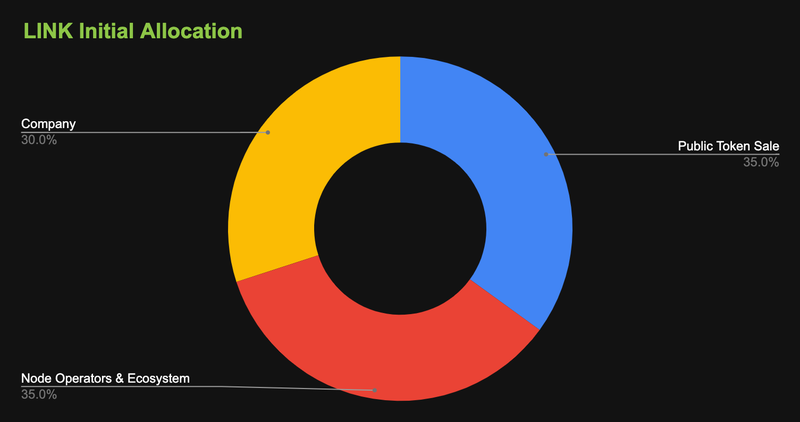
The initial token distribution of LINK token:
35% is allocated to Public Token Sale
35% is allocated to Node Operators & Ecosystem
30% is allocated to Developers Company
This means 70% of LINK token supply goes to investors, communities and node operators, while the other 30% goes to the company team.
Closing
Chainlink has emerged as a leading decentralized oracle network within the blockchain industry. It has created a secure and reliable path for smart contract applications to interact with real world data. By using a network of nodes working in collective, Chainlink makes sure that the data used by smart contracts is trustworthy and verified.
Chainlink also ensures the integrity and accuracy of data by aggregating information from multiple sources and verifying it through consensus algorithms. This enables smart contracts to make informed decisions based on real time and accurate data.
As blockchain technology evolves, Chainlink’s role as a vital infrastructure to the blockchain applications will continue to shape the future of the cryptocurrency industry.









