Aptos is one of the recent blockchain projects that has been developed since late 2021. The project itself is being developed by using the strong idea behind Meta (Facebook) digital currency called Diem, formerly Libra.
Diem, before being canceled, was bringing the idea to solve the cryptocurrency project’s trilemma, which is between decentralized, secure and scalable, which most crypto projects can only meet two of these three advantages. Let’s say Bitcoin is very decentralized and secure by sacrificing its scalability. On the other hand, projects like Ripple or Tron are very scalable and secure however they are not as decentralized as Bitcoin.
Aptos tries to combine the three crypto projects advantages by focusing on scalability, safety, reliability and upgradeability as its key principles. The project also seeks to spread awareness of Web3 and encourage widespread adoption of its features.
Many crypto community members dubbed Aptos as Solana killer, for its origins and scalability ambitions.
Introduction
Aptos was launched back in late 2022 during the bear market, it is like a tradition that many potential crypto projects launched precisely on the bear market. Take examples of BNB, MANA, Ziliqa and Theta that were launched during the 2018 bear market, and bounce back in terms of values and adoption during the 2021 bulls. In a similar fashion, Aptos was launched on the 2022 bear market and started discussion among the crypto community.
Aptos aims to bring new concepts for consensus mechanism, performance, security, smart contract design, and decentralization to the layer-1 space. Its ultimate goal is to build a blockchain that will enable widespread adoption of web3 and enable an ecosystem of DApps to address actual real-world problems.
To address these issues, Aptos dubbed itself as high-throughput Layer-1 blockchain. Aptos claims that the network’s unique parallelized and pipeline design allows the network to fully utilize all hardware resources. Multiple sharding upgrades will be able to gradually improve the network performance beyond the capacity of a single machine because of its modular architecture.
How does Aptos achieve this? We will cover the technical below
How Does Aptos Work?
Similar to other layer-1 blockchains of recent generations, Aptos utilizes a proof of stake consensus mechanism. As a result, Aptos is forced to rely on validators to handle transactions, upload new blocks, and maintain network security. Because of this, Aptos rely on validators to secure the network, complete transactions, and upload new blocks.
The fundamental building blocks of Aptos are:
1. Integration of Move programming language. Move is a Rust-based programming language with a focus on security that enables fast and safe transaction execution.
Move, a virtual machine technology used by Aptos, was first developed for Facebook’s blockchain project (Libra), however it was later canceled. Move is a virtual machine developed using the Rust programming language, which is used by NEAR, Polkadot, and Solana.
Aptos using Move programming language to achieve fast and secure execution, with simple auditability and mechanical analysis. Aptos developer team claims that Aptos has several advantages compared to the Ethereum network such as its simplicity to verify blockchain commands, and Aptos enables users to modify their private keys.
2. Modular transaction processing, transaction dissemination, block metadata ordering transaction execution, batch storage and ledger certification, all work in parallel.
The Aptos team called their scaling sharding technologies as BlockSTM, stands for Software Transactional Memory. This technology technically works similar to layer-2 machine that queues transactions on batches then verifies all those transactions in one go.
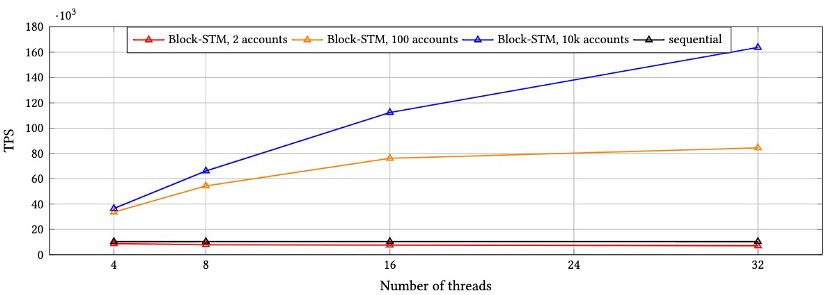
Technically, the BlockSTM implementation allows Aptos to reach 160,000 TPS during the testnet.
3. Flexible key management and hybrid custodial options, through this unique solution, Aptos aims to give users a safer and more reliable experience.
4. Atomicity without upfront knowledge of the data, as a result, Aptos can boost throughput and cut down on latency.
5. Modular blockchain architecture, allowing Aptos to offer frequent and instant upgrades to every of its network components.
As a result, Aptos can easily upgrade its network in response to issues the networks are facing. This modular architecture also enables for the APT token holders to engage in an on-chain governance system.
6. Innovative scaling solutions, Aptos supports internal sharding of a validator and homogeneous state of sharding.
Aptos uses a byzantine fault-tolerant (BFT) proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism and is built around several design principles.
Each Aptos blockchain’s transaction stages are all totally autonomous, and individually parallelizable, mimicking modern superscalar processing architectures. The blockchain is secured by the low-latency BFT consensus process, which also enables it to reach up to 160,000 transactions per second (TPS) on testnet stage. While the Ethereum network can only process about 12 – 15 TPS.
Aptos natively implements technologies similar to sharding, almost identical to future plans of Ethereum network upgrades. This allows the Aptos network to meet its upgradeability and configurability nature to maintain scalability in order to serve the new wave of crypto and Web3 adoption in the future.
Who Created Aptos?
Mo Shaikh and Avery Ching, the two people behind Aptos, are currently its CEO and CTO. Both of them previously worked as a team of developers for Meta (Facebook) Diem digital currency project. Mo Shaikh and Avery Ching have contributed to the creation of the Move programming language which was intended for Diem project before it is being canceled and being utilized on the Aptos project.
Mo Shaikh has a Master’s degree in Business Administration and Avery Ching has a PhD. in computer science.
In 2022, Aptos raised $350 million in two rounds of funding, $150 million in March, and $200 million in July. Finally Aptos network went live on 28 October 2022.
The APT Token
Aptos have their own native token named APT. Using the byzantine fault-tolerant (BFT) proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism where BFT consensus ensures a decentralized network can still operate, even when 1/3 of validators/nodes are misbehaved or offline. This PoS consensus mechanism allows APT token holders to stake their token to the validator for securing the network, and earn rewards as a return.
Currently, APT tokens sits on the top 30 of cryptocurrency’s largest market cap with more than $2 billion in valuation from 177 million of APT tokens circulating supplies.
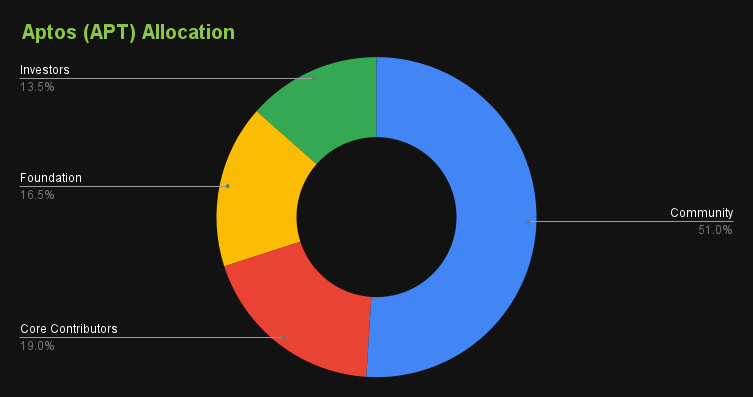
The initial distribution of APT token:
- 51.02% is allocated to Community
- 19.00% is allocated to Core Contributors
- 16.50% is allocated to Foundation
- 13.48% is allocated to Investors
Aptos has an initial supply of 1 billion APT token with maximum supply of infinite token.
The infinite maximum supply of APT tokens made APT an inflationary asset, which gained additional supply each year from its staking rewards.
Currently, the maximum staking reward rate starts at 7% annually. The maximum staking reward rate declines by 1.5% annually until a lower bound of 3.25% annually. However, through on-chain governance, all reward amounts and methods can be modified.
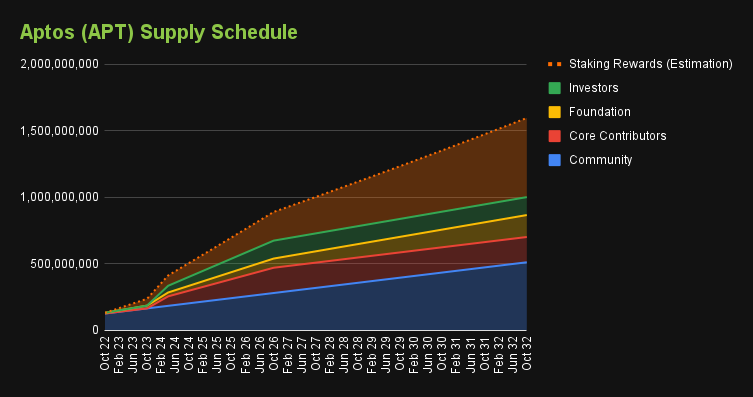
The projection of APT token supply. The chart does not anticipate staking rewards changes via public governance.
How Does Staking Work On Aptos?
The Aptos staking module defines a capability that represents ownership.
Owner
Is the owner of the funds. For example, investor A creates an account on the Aptos blockchain. Now investor A has the OwnerCapability resource. Investor A can assign his account’s operator address to the account of Validator B, a trusted node operator, to appoint Validator B as a validator. Investor A can change the node operator to another validator if he wishes to do so.
The staking rewards will be deposited into the Owner account, in this case the Investor A account.
Operator
A node operator is assigned by the fund owner to run the validator node. The two personas, the owner and the operator, can be two separate entities or the same. For example, Validator B (operator) runs the validator node, operating at the behest of Investor A, the fund owner.
Staking rewards are split between Operator and Owner.
Voter
An owner can designate a Voter. This enables the voter to participate in governance. The voter will use the voter key to sign the governance votes in the transactions.
Projects on Aptos Blockchain
1. PancakeSwap
Although PancakeSwap are Binance Chain projects, it is the top project in terms of TVL on the Aptos network.
2. LiquidSwap
LiquidSwap also DEXes on Aptos blockchain that allows users to swap stablecoins. LiquidSwap using the Layer-Zero to bridge other blockchains onto Aptos.
3. Tortuga
APT liquid staking platforms. Users can earn up to 7% APY, the same as APT annually staking rewards.
Aptos Advantages
| Newer generation blockchain projects |
| Very fast network speed, although real world use case still not yet proven |
| Developer team’s background from big companies |
| Implemented sharding-like technologies, the BlockSTM on its early stage |
| Being dubbed as ‘Solana Killer’ |
| Users are allowed to modified their own private keys |
| Relatively high staking rewards (APY up to 7%) |
Closing
Although still a relatively new project, Aptos can enter the crypto top 50 largest market cap because of its project’s concept and developer team. The powerful technology and implementation of Move programming language making Aptos can be modified quickly depending on the situations the blockchain is facing.
However investing in newer cryptocurrency projects means investors should be aware of its high price volatility as the utility of the project remains narrative and has not yet been proven.








